- Регистрация
- 17 Февраль 2018
- Сообщения
- 39 625
- Лучшие ответы
- 0
- Реакции
- 0
- Баллы
- 2 093
Offline
Cyber criminals are using AI tools to attack their victims faster and more effectively. Users must now be even more vigilant.

Image: Shutterstock/pancha.me
Summary created by Smart Answers AI
In summary:
Back in February 2025, several media outlets warned of a new threat targeting users of Google’s Gmail email service. Attackers used AI technology to perfect phishing emails and make them look more convincing.
To do this, the AI collected freely available data from social networks, websites, and online forums on the internet and used this information to formulate a deceptively genuine-looking email that pretended to come from an acquaintance, family member, or superior.
What’s more, to ensure that the message actually looked deceptively genuine, the AI also generated suitable domains as senders for the emails. The scam was dubbed “Deepphish”—a portmanteau of the terms deep learning and phishing.
Even if the report mentioned at the beginning raises some questions—such as why Gmail users in particular were affected by the Deepphish attack—it nevertheless highlights a development that experts had been expecting for some time: criminal groups are increasingly using AI tools to perfect their attacks.
Domains created with AI
One of the weak points of conventional phishing attacks has always been the sender address. Most phishing emails can be easily identified by the sender .
For example, a message from a streaming service such as Netflix or Disney with an address like
[email protected]
is almost certainly a fake—no matter how perfect the rest of the presentation may be.
In the AI-supported variant of a phishing attack, on the other hand, new types of algorithms are used that generate a sender address with a matching URL that is adapted to the text of the email.
A research group led by Alejandro Correa Bahnsen at the US company Cyxtera Technologies, an operator of data centers, investigated how effective these algorithms can be.
They developed an algorithm called Deepphish, which was trained to suggest suitable URLs for phishing attacks. To do this, they fed a neural network with more than one million URLs that had been set up for phishing via email in the past and used them to train their algorithm.
In doing so, they specified two different profiles for the actors behind the phishing attack.

Phishing emails can often be recognized by the sender addresses. If, as in this case, a message purporting to be from Disney comes from andy@ brandbot.com, something is wrong.
Foundry
With the AI-generated addresses, they achieved an increase in attack efficiency from 0.69 to 20.9 percent for one profile and from 4.91 to 36.28 percent for the other.
They published their results in a stud you can find here.
While Deepphish originally only referred to the algorithm developed at Cyxtera, it’s now used in most cases for AI-supported phishing attacks in general.
How a Deepphish attack works
Deepphish attacks follow a standardized pattern. The first step is to research the target’s social environment:
The AI uses social networks and online forums as sources, as well as data published by hackers from intrusions into company networks and websites. The more data collected in this way, the more precisely the phishing email can be tailored to the victim.
In a study, employees at Cyxtera investigated how the success rate of phishing emails can be increased by selecting an AI-generated sender address.
Foundry
The next step is to register a suitable domain and generate a sender address using an algorithm such as Deepphish.
The AI then writes the text of the email. Using the information collected, it generates a suitable subject line, a salutation tailored to the recipient and content that is worded correctly and could actually have been written by the supposed sender.
Due to the precise personalization, the message appears considerably more credible than a standard phishing email.
But what do the criminals want to achieve with their deepphish attacks? They want to inspire so much confidence with their forgeries that the recipient is prepared to click on a file attachment or an embedded link.
Everything else happens automatically: the file attachment then usually downloads and installs malware. The link, on the other hand, leads to another fake website that requests credit card details or login information for a streaming service, for example.
AI-supported phishing emails
However, the Deepphish algorithm is just the beginning. There is now a whole range of tools that do all the work for criminals when formulating phishing messages.
The programs are called FraudGPT, WormGPT, or GhostGPT. They formulate phishing emails that are targeted at individuals or specific companies.
For example, the user can instruct these programs to generate a Netflix-style email with a request to enter account details on a fake website.
Or they can have questions answered such as “How do I hack a Wi-Fi password?”.
Or they can instruct the AI to program a software keylogger that forwards all keystrokes on a computer to a server address via the internet.
Hacking tools such as WormGPT use AI to generate convincing-looking and well-formulated phishing emails. In most cases, they target specific individuals or companies.
Foundry
ChatGPT and other Large Language Models (LLMs) have in-built filters so that they do not respond to such requests. As ChatGPT does not disclose its code, there is nothing that can be done about this.
However, it is possible to use instructions from the darknet to confuse LLMs such as ChatGPT via certain prompt sequences so that they are then prepared to disregard their in-built filters.
At the same time, some criminal groups have switched to LLMs from the open source scene and removed the corresponding filters.
AI generates malware
The Stopwatch AI website demonstrates just how far the possibilities of AI-generated malware already go. It shows how AI can be used in three simple steps to program malware that specifically undermines the protective shield of the major antivirus tools.
In the first step, called “Choose Platform”, you select the operating system of the computer you want to attack. You can choose from Mac, Windows, Linux, AWS (Amazon Web Services, Amazon’s cloud service), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure, Microsoft’s professional cloud service.

The Stopwatch AI website demonstrates how malware can be programmed in a few simple steps with the help of AI tools. The first step is to select the operating system to be attacked.
Foundry
The second step is called “Choose Defence” and offers nine antivirus tools, including Microsoft Defender, Eset Endpoint Protection Advanced, McAfee Endpoint Security, Symantec Endpoint Security, and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Business.
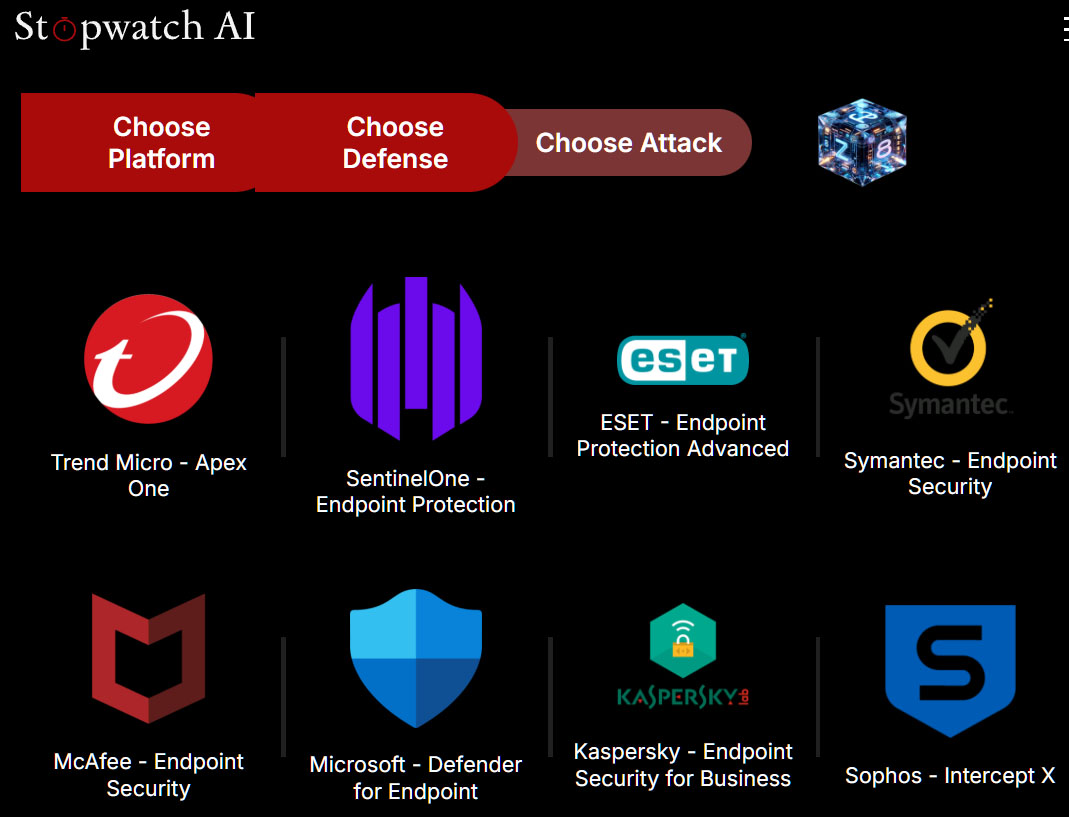
In the second step, Stopwatch AI users select the antivirus program whose weaknesses they want to exploit with their malware attack. Microsoft Defender is also listed here.
Foundry
In the third step, “Choose Attack”, you specify the type of virus you want to create. The selection ranges from adware and spyware to ransomware and keylogging through to data exfiltration, i.e. data theft.

Stopwatch AI offers ten different types of malware, from keyloggers to ransomware. The user must register in order to implement the selected malware.
Foundry
After clicking on a form of attack, Stopwatch AI asks for log-in details. It is possible to register with the site using a Google, Github, or Microsoft account. As soon as registration is complete, the AI starts programming the desired malware.
In order to use the site, the user must agree to the terms of use, which exclude attacks against other systems. This is because Stopwatch AI is only intended for studying malware development with AI.
Critically, all projects are assigned to the respective user and saved.
How to recognize AI-generated phishing emails
Always take a look at the sender address of incoming emails and consider whether it is plausible. Also look out for the following features:
Every antivirus program downloads the latest virus definitions from the manufacturer’s server at least once a day. They describe the characteristics of the new malware variants discovered in the last few hours so that the software on the user’s computer can reliably detect the malware.
However, this protective shield has become increasingly fragile. The reason: virus construction kits that allow hobby programmers to create functioning malware even without AI have been circulating on the darknet for decades—but not only there.
Many of these malware programs are simply minimally modified variants of already known viruses. The author often only has to change the signature for his malware to be counted as a new virus. This is the only way to explain why antivirus manufacturers report 560,000 new malware programs every day.
In the age of AI, the production of malware variants has taken on a new quality. This is because security manufacturers had taught their antivirus programs to recognize and isolate the variants of already known malware.
With AI support, it’s now possible to manipulate existing malware in a targeted manner so that it is no longer recognized by the virus watchdogs.
The tool manufacturer Acronis demonstrated this in a presentation using a malware sample that it had uploaded to Google’s detection service Virustotal.
While it was initially recognized as malware by nine of the antivirus programs used there, only one virus guard was able to identify the malware as such after it had been reworked by Grok3’s AI. When the researchers had the sample code processed by Gemini 2.0 Flash and Deepseek R1, the virus was no longer detected by any of the programs at Virustotal.
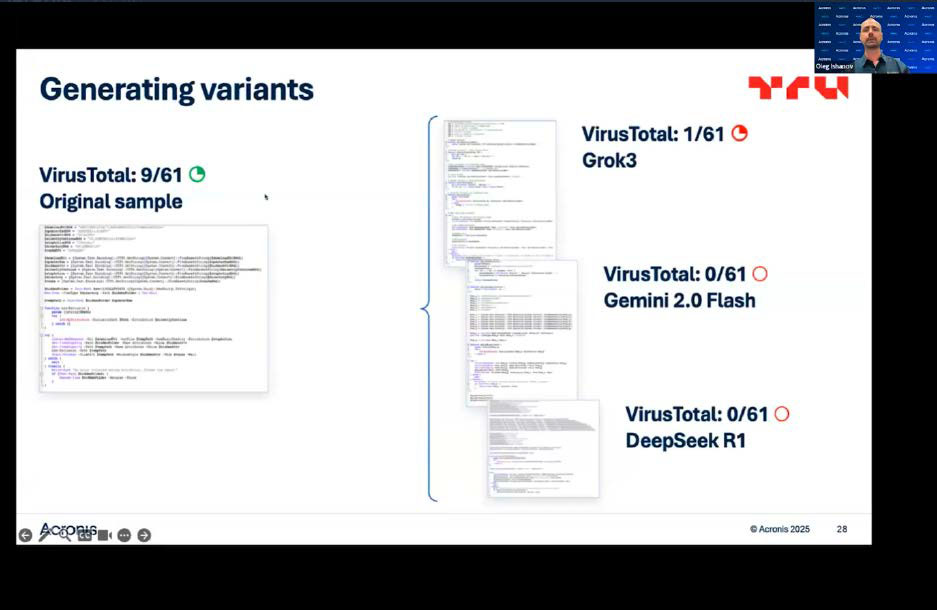
Depending on which AI software is used, the hacker can manipulate existing malware in such a way that it remains almost or even completely undetected by Virustotal.
Foundry
Nevertheless, the heuristic and behavior-based methods of antivirus programs also work with malware whose code has been modified with the help of AI.
Email spoofing
The falsification of email addresses, known as email spoofing, hardly occurs any more. Since 2014, the SPF, DKIM and DMARC authentication methods have gradually been defined as standards and subsequently implemented by email providers.
Since then, it is no longer possible to falsify the domain information in an email address. For an address such as “[email protected]”, for example, the domain is pcworld.com. If the aforementioned authentication procedures are deactivated by a provider, these mails are normally sorted out as spam by the recipient.
Spoofing attempts still exist, however. The sender’s name can be changed in many e-mail clients, for example in classic Outlook via File -> Account settings -> Account settings -> Change -> Your name.
However, this does not affect the email address. In the case of hacker attacks, the reply address is sometimes changed at the same point. In this way, all replies to the emails sent are sent to the hacker’s address. Another trick is to use a similar-looking domain, such as “[email protected]“.
This article originally appeared on our sister publication PC-WELT and was translated and localized from German.
Author: Roland Freist, Contributor, PCWorld

Roland Freist is a freelance IT journalist covering topics related to Windows, applications, networks, security and the Internet.
Recent stories by Roland Freist:

Image: Shutterstock/pancha.me
Summary created by Smart Answers AI
In summary:
- PCWorld reports that AI-powered “Deepphish” attacks are dramatically increasing phishing success rates, with effectiveness jumping from 0.69% to 20.9% by using personalized content gathered from social media.
- Criminal AI tools like FraudGPT and WormGPT bypass ethical filters to create convincing phishing emails with realistic sender domains, specifically targeting Gmail users with urgent requests.
- AI-generated malware can now evade major antivirus detection, with tools like Stopwatch AI demonstrating how malware variants can go from 9 detections to zero on security platforms.
Back in February 2025, several media outlets warned of a new threat targeting users of Google’s Gmail email service. Attackers used AI technology to perfect phishing emails and make them look more convincing.
To do this, the AI collected freely available data from social networks, websites, and online forums on the internet and used this information to formulate a deceptively genuine-looking email that pretended to come from an acquaintance, family member, or superior.
What’s more, to ensure that the message actually looked deceptively genuine, the AI also generated suitable domains as senders for the emails. The scam was dubbed “Deepphish”—a portmanteau of the terms deep learning and phishing.
Even if the report mentioned at the beginning raises some questions—such as why Gmail users in particular were affected by the Deepphish attack—it nevertheless highlights a development that experts had been expecting for some time: criminal groups are increasingly using AI tools to perfect their attacks.
Domains created with AI
One of the weak points of conventional phishing attacks has always been the sender address. Most phishing emails can be easily identified by the sender .
For example, a message from a streaming service such as Netflix or Disney with an address like
[email protected]
is almost certainly a fake—no matter how perfect the rest of the presentation may be.
In the AI-supported variant of a phishing attack, on the other hand, new types of algorithms are used that generate a sender address with a matching URL that is adapted to the text of the email.
A research group led by Alejandro Correa Bahnsen at the US company Cyxtera Technologies, an operator of data centers, investigated how effective these algorithms can be.
They developed an algorithm called Deepphish, which was trained to suggest suitable URLs for phishing attacks. To do this, they fed a neural network with more than one million URLs that had been set up for phishing via email in the past and used them to train their algorithm.
In doing so, they specified two different profiles for the actors behind the phishing attack.

Phishing emails can often be recognized by the sender addresses. If, as in this case, a message purporting to be from Disney comes from andy@ brandbot.com, something is wrong.
Foundry
With the AI-generated addresses, they achieved an increase in attack efficiency from 0.69 to 20.9 percent for one profile and from 4.91 to 36.28 percent for the other.
They published their results in a stud you can find here.
While Deepphish originally only referred to the algorithm developed at Cyxtera, it’s now used in most cases for AI-supported phishing attacks in general.
How a Deepphish attack works
Deepphish attacks follow a standardized pattern. The first step is to research the target’s social environment:
- Where does she live?
- Where does she work?
- What are the names of their family members?
- What are their friends’ names?
- What are the names of their colleagues and superiors?
- What are their email addresses, how close are they to the target person?
The AI uses social networks and online forums as sources, as well as data published by hackers from intrusions into company networks and websites. The more data collected in this way, the more precisely the phishing email can be tailored to the victim.

In a study, employees at Cyxtera investigated how the success rate of phishing emails can be increased by selecting an AI-generated sender address.
Foundry
The next step is to register a suitable domain and generate a sender address using an algorithm such as Deepphish.
The AI then writes the text of the email. Using the information collected, it generates a suitable subject line, a salutation tailored to the recipient and content that is worded correctly and could actually have been written by the supposed sender.
Due to the precise personalization, the message appears considerably more credible than a standard phishing email.
But what do the criminals want to achieve with their deepphish attacks? They want to inspire so much confidence with their forgeries that the recipient is prepared to click on a file attachment or an embedded link.
Everything else happens automatically: the file attachment then usually downloads and installs malware. The link, on the other hand, leads to another fake website that requests credit card details or login information for a streaming service, for example.
AI-supported phishing emails
However, the Deepphish algorithm is just the beginning. There is now a whole range of tools that do all the work for criminals when formulating phishing messages.
The programs are called FraudGPT, WormGPT, or GhostGPT. They formulate phishing emails that are targeted at individuals or specific companies.
For example, the user can instruct these programs to generate a Netflix-style email with a request to enter account details on a fake website.
Or they can have questions answered such as “How do I hack a Wi-Fi password?”.
Or they can instruct the AI to program a software keylogger that forwards all keystrokes on a computer to a server address via the internet.

Hacking tools such as WormGPT use AI to generate convincing-looking and well-formulated phishing emails. In most cases, they target specific individuals or companies.
Foundry
ChatGPT and other Large Language Models (LLMs) have in-built filters so that they do not respond to such requests. As ChatGPT does not disclose its code, there is nothing that can be done about this.
However, it is possible to use instructions from the darknet to confuse LLMs such as ChatGPT via certain prompt sequences so that they are then prepared to disregard their in-built filters.
At the same time, some criminal groups have switched to LLMs from the open source scene and removed the corresponding filters.
AI generates malware
The Stopwatch AI website demonstrates just how far the possibilities of AI-generated malware already go. It shows how AI can be used in three simple steps to program malware that specifically undermines the protective shield of the major antivirus tools.
In the first step, called “Choose Platform”, you select the operating system of the computer you want to attack. You can choose from Mac, Windows, Linux, AWS (Amazon Web Services, Amazon’s cloud service), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure, Microsoft’s professional cloud service.

The Stopwatch AI website demonstrates how malware can be programmed in a few simple steps with the help of AI tools. The first step is to select the operating system to be attacked.
Foundry
The second step is called “Choose Defence” and offers nine antivirus tools, including Microsoft Defender, Eset Endpoint Protection Advanced, McAfee Endpoint Security, Symantec Endpoint Security, and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Business.

In the second step, Stopwatch AI users select the antivirus program whose weaknesses they want to exploit with their malware attack. Microsoft Defender is also listed here.
Foundry
In the third step, “Choose Attack”, you specify the type of virus you want to create. The selection ranges from adware and spyware to ransomware and keylogging through to data exfiltration, i.e. data theft.

Stopwatch AI offers ten different types of malware, from keyloggers to ransomware. The user must register in order to implement the selected malware.
Foundry
After clicking on a form of attack, Stopwatch AI asks for log-in details. It is possible to register with the site using a Google, Github, or Microsoft account. As soon as registration is complete, the AI starts programming the desired malware.
In order to use the site, the user must agree to the terms of use, which exclude attacks against other systems. This is because Stopwatch AI is only intended for studying malware development with AI.
Critically, all projects are assigned to the respective user and saved.
How to recognize AI-generated phishing emails
Always take a look at the sender address of incoming emails and consider whether it is plausible. Also look out for the following features:
- Become wary of emails from people you are not normally in contact with or have not heard from in a while. This is especially true if these messages contain unusual requests or enquiries.
- Hover your mouse over any links and check where they lead to. If the address does not match the sender of the email or the text of the message, it is often a scam.
- No bank, streaming service, or public authority ever asks for your password or wants to know your account details via email.
- Be suspicious of emails that put you under time pressure or claim a high level of urgency.
Every antivirus program downloads the latest virus definitions from the manufacturer’s server at least once a day. They describe the characteristics of the new malware variants discovered in the last few hours so that the software on the user’s computer can reliably detect the malware.
However, this protective shield has become increasingly fragile. The reason: virus construction kits that allow hobby programmers to create functioning malware even without AI have been circulating on the darknet for decades—but not only there.
Many of these malware programs are simply minimally modified variants of already known viruses. The author often only has to change the signature for his malware to be counted as a new virus. This is the only way to explain why antivirus manufacturers report 560,000 new malware programs every day.
In the age of AI, the production of malware variants has taken on a new quality. This is because security manufacturers had taught their antivirus programs to recognize and isolate the variants of already known malware.
With AI support, it’s now possible to manipulate existing malware in a targeted manner so that it is no longer recognized by the virus watchdogs.
The tool manufacturer Acronis demonstrated this in a presentation using a malware sample that it had uploaded to Google’s detection service Virustotal.
While it was initially recognized as malware by nine of the antivirus programs used there, only one virus guard was able to identify the malware as such after it had been reworked by Grok3’s AI. When the researchers had the sample code processed by Gemini 2.0 Flash and Deepseek R1, the virus was no longer detected by any of the programs at Virustotal.

Depending on which AI software is used, the hacker can manipulate existing malware in such a way that it remains almost or even completely undetected by Virustotal.
Foundry
Nevertheless, the heuristic and behavior-based methods of antivirus programs also work with malware whose code has been modified with the help of AI.
Email spoofing
The falsification of email addresses, known as email spoofing, hardly occurs any more. Since 2014, the SPF, DKIM and DMARC authentication methods have gradually been defined as standards and subsequently implemented by email providers.
Since then, it is no longer possible to falsify the domain information in an email address. For an address such as “[email protected]”, for example, the domain is pcworld.com. If the aforementioned authentication procedures are deactivated by a provider, these mails are normally sorted out as spam by the recipient.
Spoofing attempts still exist, however. The sender’s name can be changed in many e-mail clients, for example in classic Outlook via File -> Account settings -> Account settings -> Change -> Your name.
However, this does not affect the email address. In the case of hacker attacks, the reply address is sometimes changed at the same point. In this way, all replies to the emails sent are sent to the hacker’s address. Another trick is to use a similar-looking domain, such as “[email protected]“.
This article originally appeared on our sister publication PC-WELT and was translated and localized from German.
Author: Roland Freist, Contributor, PCWorld

Roland Freist is a freelance IT journalist covering topics related to Windows, applications, networks, security and the Internet.
Recent stories by Roland Freist:
